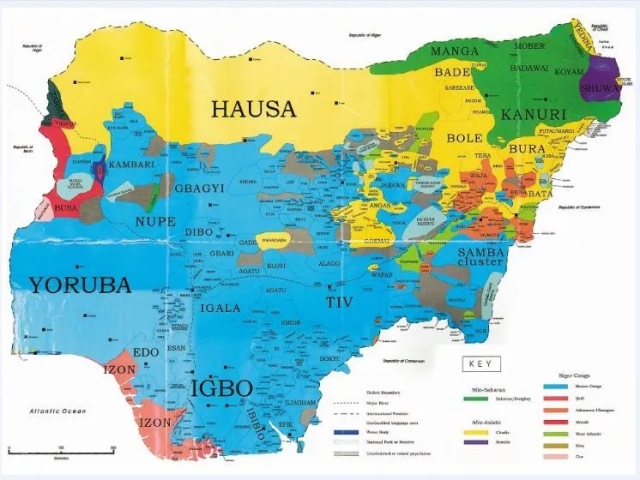
Nigeria is a country of over 200 million people and 500 indigenous languages, making it one of the most linguistically diverse countries in the world. From Hausa in the north to Igbo in the southeast, each language reflects its own unique cultural heritage.
This article will explore how these fascinating languages are shaped by their history, traditions, and way of life. Discover what makes them so special as you take an exciting linguistic adventure into Nigeria’s diverse linguistic landscape!
Overview of Nigeria’s Linguistic Landscape
These Nigerian languages are distributed across the country, with each region having its dominant language(s).

Indigenous Languages in Nigeria
The exact number of Nigeria’s languages is uncertain due to the difficulty of identifying and documenting some of the lesser-known languages. But there are at least 500 different languages in the West African country.
The majority of these languages belong to the Niger-Congo language family, which is one of the largest language families in Africa. The most commonly spoken Nigerian languages include Hausa, Yoruba, Igbo, Fulfulde, Kanuri, Tiv, Edo, and Efik.
Distribution of Languages Across Nigeria
Innovative Tech Solutions, Tailored for You
Our leading tech firm crafts custom software, web & mobile apps, designed with your unique needs in mind. Elevate your business with cutting-edge solutions no one else can offer.
Start NowIn Nigeria, Hausa is dominant in the north, Yoruba in the southwest, and Igbo in the southeast. The country’s central region is home to various minority languages, including Tiv, Idoma, and Berom.
In the south-south region, the dominant languages are Efik, Ibibio, and Urhobo. The linguistic diversity in Nigeria contributes to the country’s cultural richness and provides a unique cultural experience for visitors.
Major Languages in Nigeria
Nigeria has three major languages, Hausa, Yoruba, and Igbo.
Hausa Language
Hausa is one of the most widely spoken languages in Nigeria and is predominantly spoken in the northern region of the country.
It is a member of the Chadic language family and is also spoken in other West African countries such as Ghana, Chad, and Cameroon.
Hausa is a tonal language, meaning that pitch differences can change the meaning of words. It is written using the Latin alphabet and has a rich literary tradition, with works of literature dating back several centuries.
Yoruba Language
Yoruba is spoken in the southwestern region of Nigeria. It is a member of the Volta-Niger language family and has several dialects. Yoruba, just like the Hausa language is tonal; the pitch differences can change the meaning of words.
It is written using the Latin alphabet and has a rich oral tradition, including proverbs, folktales, and other forms of verbal art. Yoruba has also been used in literature, music, and film.
Igbo Language
Igbo is a tonal language spoken in the southeastern region of Nigeria. It is a member of the Volta-Niger language family too, and it has several dialects.
It is written using a combination of Latin and special characters. Igbo has a rich oral tradition, including proverbs, folktales, and other forms of verbal art. It has also been used in literature, music, and film.
Besides the significant languages mentioned above, there are several other lesser-known languages spoken in Nigeria.
These include Fulfulde, Kanuri, Tiv, Edo, Efik, Idoma, Berom, Ibibio, and Urhobo. Fulfulde and Kanuri are predominantly spoken in the country’s northern region, while Tiv is spoken in the central region. Edo is spoken in the southwestern region, while Efik, Idoma, Berom, Ibibio, and Urhobo are spoken in the south-south region.
Seamless API Connectivity for Next-Level Integration
Unlock limitless possibilities by connecting your systems with a custom API built to perform flawlessly. Stand apart with our solutions that others simply can’t offer.
Get StartedRead: The Rich Diversity of African Languages and Their Importance
The Significance of Language in Nigeria’s Culture
Language plays a significant role in Nigerian culture. It is a means of communication and is also used for preserving cultural heritage.
Nigerian languages are rich in proverbs, folktales, and other forms of verbal art passed down from generation to generation.
Language is also used to express religious beliefs, cultural values, and societal norms. It is not uncommon for Nigerians to switch between different languages depending on the context or situation, highlighting the importance of language in everyday life.
Challenges in Documenting Nigerian Languages
Documenting Nigerian languages is a challenge due to the country’s linguistic diversity and limited resources for language documentation. Some languages are on the brink of extinction due to the lack of documentation and preservation efforts.
Many Nigerian languages have yet to be fully described and analyzed, and their grammatical structures and linguistic features are yet to be fully understood.
Unique Features of Nigerian Languages
Tonal Languages
One of the most distinctive features of Nigerian languages is that many of them are tonal. This means that the pitch or tone of a word can change its meaning.
For example, in Yoruba, the word “oko” can mean “husband” when pronounced with a high tone, but it means “farm” when pronounced with a low tone.
Similarly, in Igbo, the word “nwa” can mean “child” when pronounced with a high tone, but it means “death” when pronounced with a low tone.
This feature makes Nigerian languages particularly challenging for non-native speakers to learn.

Complex Verb System
Nigerian languages also have a complex verb system that includes various affixes, tense markers, and mood markers.
For example, in Hausa, a verb can have up to 14 different forms, depending on its tense, aspect, and mood. In Yoruba, the verb system includes tense markers that distinguish between the past, present, and future, as well as mood markers that indicate whether a statement is a question, a command, or a suggestion.
Transform Business with Custom CRM & ERP Solutions
Elevate your operations with a CRM or ERP tailored for you. Let’s build the perfect solution that others can't replicate—crafted to match your business's needs like no other.
Get StartedOral Tradition
Many Nigerian languages have a rich oral tradition, which includes proverbs, folktales, and other forms of verbal art. These stories are often used to teach moral lessons, pass down cultural values, and entertain.
In Yoruba, for example, proverbs are an important part of everyday communication and are used to convey wisdom and insights. Similarly, in Igbo, folktales are used to teach children about the values of hard work, honesty, and respect.
Incorporation of Foreign Words
Nigerian languages have also incorporated words from other languages, such as English, Arabic, and French. This is because of the country’s history of colonization, trade, and cultural exchange with other countries.
For example, in Yoruba, the word for “school” is “sukuru,” which comes from the English word “school.”
Read: The Diversity of Nigerian Tribes: A Look at the Unique Cultures and Traditions
Preservation of Nigerian Languages
Preserving Nigerian languages is a critical issue that has gained increasing attention in recent years. Nigerian languages face the threat of extinction due to various factors, such as the dominance of English, urbanization, and globalization.
However, efforts are being made to preserve and promote Nigerian languages.
One of the ways to preserve Nigerian languages is through education. Many schools in Nigeria now offer language classes in indigenous languages as part of their curriculum.
This helps to promote the use of local languages among young people and encourages them to take pride in their cultural heritage. In addition, some universities in Nigeria have established language departments to promote research and teaching of Nigerian languages.
Another way to preserve Nigerian languages is through the use of technology. Technological advancement has made it easier to record, store and share information in different languages.
Several online resources and mobile applications now provide language learning resources for Nigerian languages. For example, the African Storybook project is an online platform that provides children’s stories in different Nigerian languages.
Furthermore, cultural festivals and events provide a platform for promoting Nigerian languages. These events provide an opportunity for people to showcase their cultural heritage through dance, music, and storytelling. They also help to raise awareness about the importance of preserving Nigerian languages and the need to pass them on to future generations.
The government has also recognized the importance of preserving Nigerian languages and has taken steps to support their preservation.
For example, the National Institute for Nigerian Languages was established to promote the research, teaching, and development of Nigerian languages. In addition, the National Language Centre was set up to provide language planning, research, and development services.
Tailored Tech Solutions to Drive Your Business Forward
Maximize your business potential with custom tech strategies. We deliver bespoke solutions that others can’t match, designed to solve your specific challenges with precision and impact.
Contact UsImportance of Exploring Nigeria’s Linguistic Diversity
Exploring Nigeria’s linguistic diversity is important for several reasons. Firstly, exploring Nigeria’s linguistic diversity promotes cultural understanding and appreciation.

Languages are an essential part of a culture, and exploring them can help people gain a deeper understanding of the traditions, beliefs, and values of different ethnic groups in Nigeria. It can also promote tolerance and respect for other cultures, which is vital for building a more peaceful and harmonious society.
Secondly, exploring Nigeria’s linguistic diversity can contribute to the preservation of endangered languages. Many Nigerian languages are at risk of extinction, and exploring them can help raise awareness of their value and importance.
It can also help to identify ways to promote and preserve them for future generations.
Additionally, exploring Nigeria’s linguistic diversity can have economic benefits. With Nigeria’s growing economy, there is a need for more language professionals to cater to the needs of the various ethnic groups in the country.
Exploring Nigerian languages can help create opportunities for language professionals, such as translators and interpreters, to bridge communication gaps and facilitate trade and commerce.
Lastly, exploring Nigeria’s linguistic diversity can promote education and literacy. Many Nigerian children grow up speaking their local languages but are often taught in English at school. Exploring Nigerian languages can help to develop teaching materials in local languages, making education more accessible to children and promoting literacy in local languages.
Before you go…
Hey, thank you for reading this blog to the end. I hope it was helpful. Let me tell you a little bit about Nicholas Idoko Technologies. We help businesses and companies build an online presence by developing web, mobile, desktop, and blockchain applications.
We also help aspiring software developers and programmers learn the skills they need to have a successful career. Take your first step to becoming a programming boss by joining our Learn To Code academy today!











