Last Updated on December 26, 2022
The impact of European colonialism on African societies and culture was profound. It led to the displacement of indigenous cultures and the imposition of new systems of government, law, and education. It also significantly impacted the economic development of African countries, which is still evident today.
We cannot continue to blame colonialism for Africa’s woes. Still, you would agree that much of the continent’s problems started with Western invasion. Many African countries struggle to develop economically and are plagued by political instability. Additionally, colonialism’s legacy often overshadows the continent’s rich cultural heritage.
Despite the challenges, many African countries are thriving. This is partly because the continent is home to many natural resources. Additionally, many African countries are embracing their cultural heritage and working to promote it on the global stage.

African Imperialism Under European Rule
In the 19th century, modern European imperialism in Africa saw European imperial nations take power, conquer, and rule the majority of the African continent. European nations created cutting-edge technologies during this time, which improved their capacity to project their influence internationally. In addition, Europeans became more interested in Africa to advance themselves.
The Scramble for Africa officially began in 1884, although European colonial expansion in Africa had already started before this year. The Scramble for Africa is when European nations swiftly acquired control of sizable portions of the continent. Major imperial countries met in Berlin that year for the Berlin Conference. There, they decided on a set of guidelines that respected one another’s imperialist goals.
Read: Facts About Ancient Egyptians That European Colonialism Has Misconstrued
Why Europe Colonized Africa
There were various reasons why European nations colonized Africa. Imperialists publicly defended colonizing Africa on the grounds of humanitarianism, philanthropy, and the expansion of Christianity. European leaders claimed that colonialism would help Africans because their continent was less developed than Europe.
Missionaries worked to propagate Christianity throughout Africa to protect Africans from their supposedly deceitful polytheistic beliefs and Islam.
However, Europe did not occupy Africa for the sole purpose of these feeble claims. Self-centered goals on the part of European colonial rulers actually drove the Scramble for Africa. All they wanted was to profit from Africa’s riches and seek control over new territories to strengthen their position in the imperial hierarchy.
Many European leaders of this era practiced biological racism. And thought that the people of Africa were incapable of self-government and should not be allowed to. Missionaries, explorers, and independent traders traveled the continent before imperial governments colonized large portions of Africa. Africa became more popular as a result of the press coverage of these expeditions in Europe.
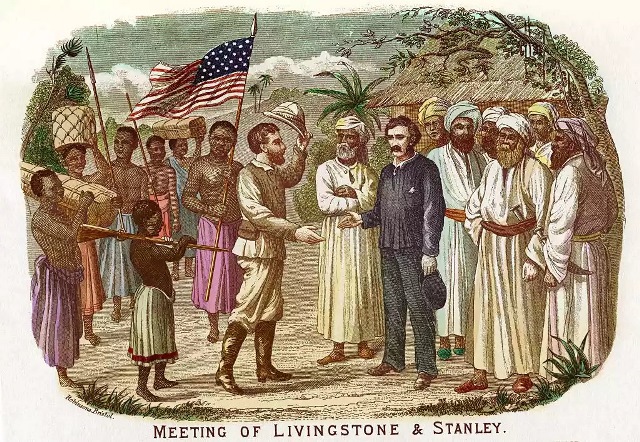
David Livingstone, who traveled most of central Africa, was the most well-known of these explorers and missionaries. Adventurer Henry Morton Stanley was sent to locate Livingstone after losing touch with Europe for six years. King Leopold II of Belgium was able to colonize that area thanks to Stanley’s involvement in exploring the Congo River.

The Scramble for Africa and Colonialism
Numerous factors led to the Scramble for Africa. Technological advancements are possibly the most convincing justification for why it occurred at the time it did. Europe did not entirely outmatch the African governments that resisted European conquest in the past.
Due to their high risk of contracting tropical diseases, Europeans could not travel extensively in Africa. The 19th century, however, saw significant technological developments that improved Europe’s capacity to colonize Africa. Steamships, railroads, telegraphs, and the discovery of quinine all contributed to the efficiency of European soldiers and reduced their distance from their sources of supply.
As was already established, the imperial rivalry was another reason for taking control of Africa. Even though the British Empire dominated the continent at the time, other European powers like Germany and France believed that seizing control of portions of Africa would help them stand a better chance of competing with Britain.
In fact, these imperial powers nearly started wars with one another for control of these distant lands – Britain and France almost started a war in 1898 over Sudan, while Britain, France, and Germany almost started a war in 1906 over Morocco.
Read: What is the 1884 Berlin Conference and its Impact on Africa Today?
The Economic and Political Impacts of Colonialism on Africa
Since the 1500s, African societies have been impacted by European colonialism. Colonialism’s economic and political impacts have been profound and can still be seen in many African countries today.
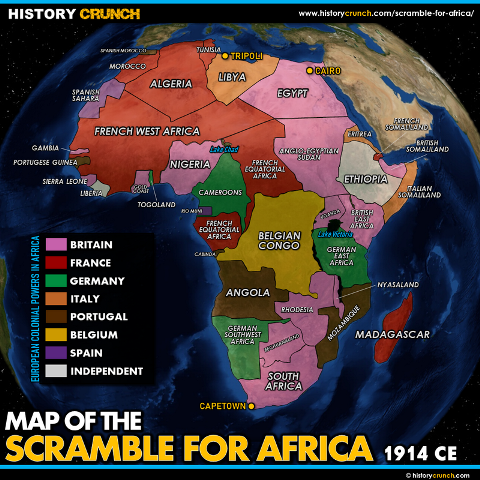
Colonialism changed the way that African societies were structured and governed. It also significantly impacted the economy, as African countries were forced to produce raw materials for European markets. This led to a decline in local manufacturing and a reliance on imports.
The political impacts of colonialism were also far-reaching. African countries were divided up into colonies, and African people were denied their basic rights and freedoms. This had a devastating impact on African societies and is still felt in many African countries today.
Furthermore, the political and economic landscape of modern-day Africa has been influenced by colonialism. African nations today follow a model similar to that of the west. Most African nations embraced their European invaders’ more authoritarian and centralized organizational structure.
Realistically, ethnic exclusion and marginalization are hallmarks of post-independence African politics. And Africa tends to favor one-party systems, and even despite the emergence of alternative parties, their ability to operate is severely constrained. Additionally, the colonial era also impacted the corrupt actions of modern African leaders.
Colonizers heavily used the economic potential of African resources. This makes Africa less competitive and weaker in its interactions with the global economy.
Read: What Happened During Apartheid in South Africa?
The Impacts of European Colonialism On African Culture
The European colonization of Africa began in earnest in the late 19th century, and for nearly a century, African societies were bombarded with foreign cultural influences. This period of colonialism had a profound and lasting impact on African cultures.
The arrival of Europeans in Africa coincided with the introduction of new technologies, ideas, and values. African societies were quick to adopt these new technologies, but they were also often forced to adopt new economic, political, and social systems that were designed to benefit the colonists.
In many cases, African cultures were completely changed by the experience of colonialism. Traditional values and beliefs were discredited, and African languages and cultures were suppressed. The colonial powers also carved up and redefined African societies, which often created artificial borders that have caused problems to this day.
Despite all of these negative impacts, there are also some positive aspects to the cultural legacy of colonialism in Africa. For instance, the introduction of new technologies and ideas has led to a more modern and globalized Africa. And in some cases, the experience of colonialism has also resulted in a new sense of African identity.
The Impacts of European Colonialism On African Societies
The impact of European colonialism on African societies is a controversial and widely-debated topic. The effects of colonialism on Africa are varied and complex; they can be positive, negative, or a mix of both. Overall, the impact of colonialism on Africa has been largely negative.
One of colonialism’s most significant social impacts was the introduction of new religions. Christianity and Islam were brought to Africa by European colonialists, and they quickly took root in African societies. Today, Christianity and Islam are the two largest religions in Africa.
Another social effect of colonialism was the disruption of traditional African societies. African societies were typically organized around kinship groups, and the colonial rule changed that. Under colonialism, African societies were reorganized around European ideas of Individualism and private property. This had a profound impact on the way Africans viewed themselves and their place in society.
The social impacts of colonialism are still being felt today, more than a century after the last African colony was independent. African societies are still grappling with the legacy of colonialism, and it will take time for the full effects of colonialism to be controlled or stabilized.
Read: Will Great Britain Ever Return the Stolen Treasures from Africa?
Other Impacts of European Colonialism On African Culture and Society

The Colonial Masters introduced the use of Currencies to Africans
Before the advent of colonization, trade by barter was the only means of exchange in Africa. Africans were first exposed to the use of money by colonial masters, who also educated them on its potential to resolve trade by barter issues
. Then, British authorities first issued silver coins in 1912, the same year that the West African Currency Board was established. They also introduced to Africans the financial system. A number of issues with the trade-by-barter system were resolved when banks were established to hold money. This was a development that Africans really admired.
Cultural Imperialism
Things Fall Apart by Chinua Achebe has a lot to say about this. From the book, we can see how the colonial rulers saw African culture as inferior and their own as superior.
They modified anything that wasn’t in their favor, disregarded African culture, and convinced naive Africans that the new culture was better. Today, foreign languages have taken the role of Africans’ native tongues, as have their indigenous faiths, names, schools, clothes, music, and sports.
Before you go…
Hey, thank you for reading this blog to the end. I hope it was helpful. Let me tell you a little bit about Nicholas Idoko Technologies. We help businesses and companies build an online presence by developing web, mobile, desktop, and blockchain applications.
We also help aspiring software developers and programmers learn the skills they need to have a successful career. Take your first step to becoming a programming boss by joining our Learn To Code academy today!
Be sure to contact us if you need more information or have any questions! We are readily available.











