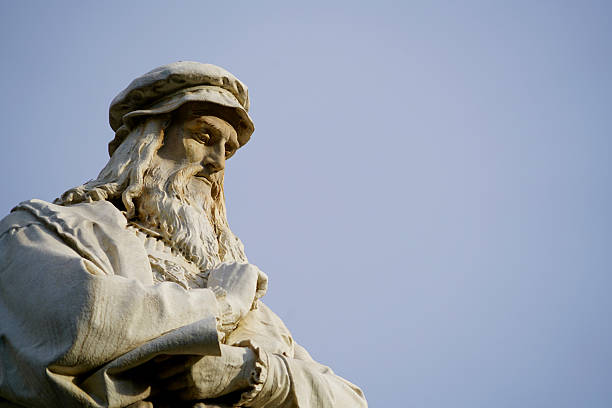
While Leonardo da Vinci is most recognised for his paintings, his work as a scientist and inventor distinguishes him as a true Renaissance man. He serves as an example of how the scientific approach may be applied to all aspects of life, including art and music. Leonardo da Vinci is primarily recognised for his dramatic and emotive artwork, but he also carried out dozens of carefully planned experiments and invented futuristic devices that were revolutionary at the time.
He made crucial scientific discoveries as a result of his keen eye and quick mind, but he never publicized his findings. Despite being a vegetarian who adored animals and detested war, he worked as a military engineer, developing innovative and lethal weaponry. Despite being one of the best painters of the Italian Renaissance, he only left a few completed works.
Keep reading to learn more about how much of a multifaceted genius Leonardo Da Vinci was.
Da Vinci — The Artist
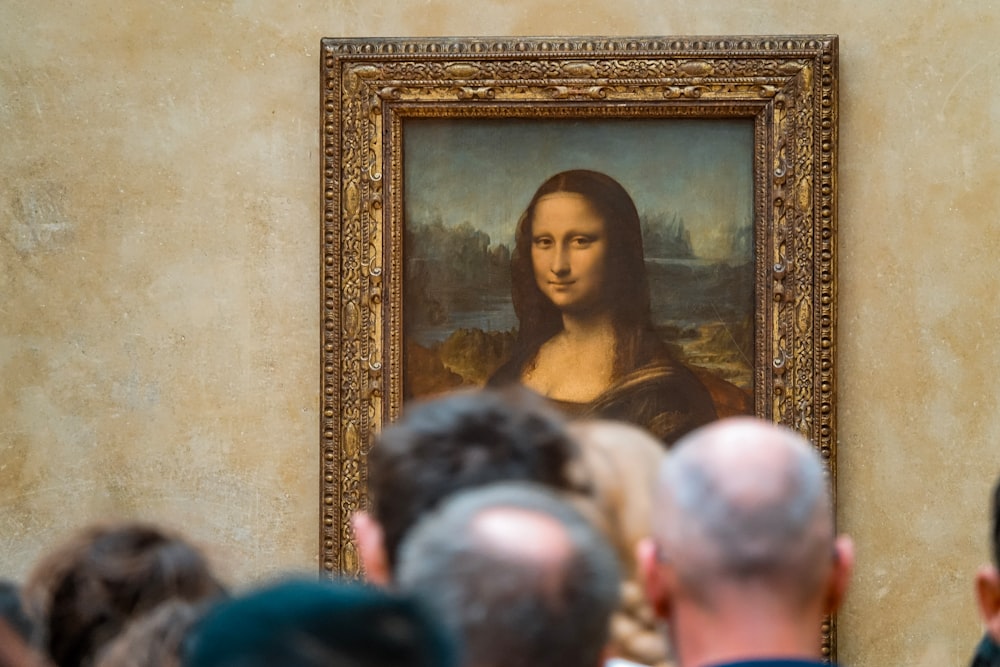

Renaissance Paintings
During the Renaissance, Leonardo da Vinci studied painting and became a great master of the medium.
European artists began to study nature more thoroughly throughout the Renaissance, with the objective of painting realistic depictions of the world. These artists learnt how to depict lifelike people and animals, as well as how to use linear perspective techniques to give a sense of depth and distance on flat walls and canvases.
Da Vinci’s talents of observation and skill as an illustrator allowed him to recognise and imitate natural phenomena, giving his portraits a unique vibrancy. Curiosity drove Leonardo to try to explain all he observed. We know he was among the first to adopt a scientific approach to studying how our world works and how we see it because he wrote down and sketched so many of his observations in his notebooks.
Realism through Observation
Leonardo realised that one approach to painting realistic subjects was to carefully examine how animals, people, and landscapes actually appeared. He was also aware of the changes in how an object seemed when seen up close versus far away, and when seen in bright versus dim light. Throughout his life, he kept comprehensive notes on his observations and produced sketches of what he saw in his notebooks.
Open Window Perspective
Architects and painters in Italy throughout the Renaissance researched how to draw three-dimensional objects on flat surfaces. They came to consider a painting to be an “open window” through which the observer might perceive the painted environment. They also devised a set of mathematical rules known as the linear perspective to aid painters in achieving their realism objectives. While working as an apprentice in Andrea del Verrocchio’s studio, Leonardo learnt the concepts of perspective and practised sketching perspective accurately utilising the window.
Da Vinci — The Mathematician
Da Vinci saw himself as a science rather than an artist. Mathematics – namely, perspective, symmetry, proportions, and geometry – had a big influence on his drawings and paintings, and he was much ahead of his time when it came to using it.
To create a sense of depth on a flat surface, Da Vinci used the mathematical principles of linear perspective – parallel lines, the horizon line, and a vanishing point. He uses perspective to accentuate the corner of a building, a walled garden, and a path in The Annunciation, for example.

Leonardo da Vinci’s The Last Supper exemplifies the use of perspective mathematics. The architectural design surrounding Jesus and the 12 apostles, along with floor lines beneath the table, creates a “vanishing point” providing a subconscious focal point for the painting.
In discussing Leonardo’s later work, we can’t overstate the significance of mathematics. He seems engrossed with these matters; for instance, while working on the Mona Lisa, reports suggest Leonardo focused on geometry, declaring, “Let no one read me who is not a mathematician.”
Da Vinci — The Inventor
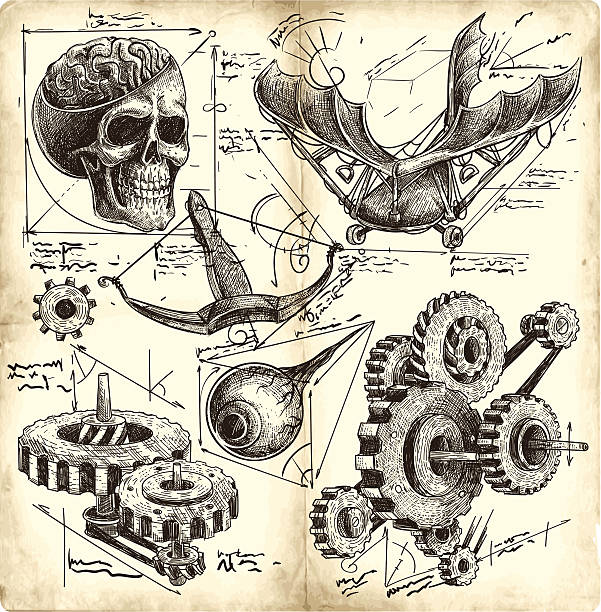
Leonardo’s artists and craftsmen were skilled in the construction and maintenance of common machinery. Inventing new types of machinery, on the other hand, would not have occurred to them.
Leonardo devised a novel approach to machines. He reasoned that if he understood how each individual machine part functioned, he could change and combine them in many ways to improve current machines or build novel ones.
Leonardo’s obsession with machinery most likely began when he was a child. Some of his first illustrations clearly demonstrate the operation of various machine sections. Leonardo observed and utilised a number of devices as an apprentice in the studio of the artist Verrocchio. He got practical knowledge of their design and structure by studying them.
Innovative Tech Solutions, Tailored for You
Our leading tech firm crafts custom software, web & mobile apps, designed with your unique needs in mind. Elevate your business with cutting-edge solutions no one else can offer.
Start NowLeonardo aimed to develop the first comprehensive explanations of machine operations and component assembly. His illustrative skills allowed him to depict his mechanical concepts with remarkable clarity. Many of his designs, even 500 years later, serve as effective blueprints for building working models.
Leonardo sketched and described ideas centuries before their actual invention. However, it seems that few of them were built and tested during his lifetime. Although his notes suggest he intended to organize and share his ideas, he passed away before accomplishing this. After his death, his notebooks were hidden, misplaced, or lost, causing his brilliant ideas to be forgotten. It took other inventors centuries to conceive similar ideas and implement them.
Da Vinci — The Scientist
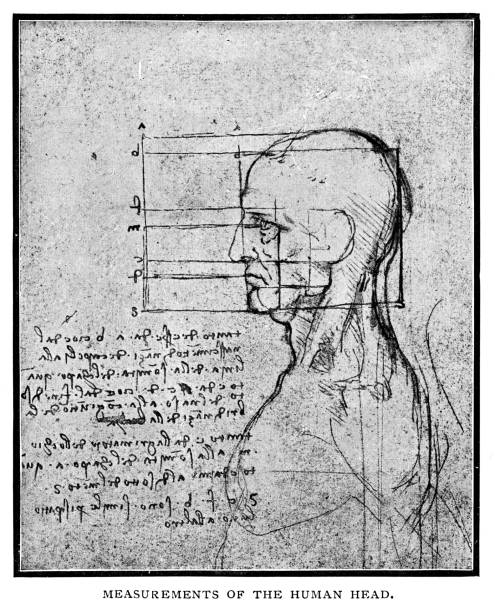
Leonardo’s work spanned the gap between mediaeval methods that were not scientific and our own modern approach. His experiments in anatomy and the study of fluids, for example, far exceeded those of his forefathers. Leonardo got increasingly engrossed in his scientific inquiries beginning with his first stay in Milan and accelerating around 1505.
His research included a wide range of subjects, including anatomy, biology, botany, geology, optics, aerodynamics, and hydrodynamics, among others.
Despite being highly influenced by ancient Greek and Roman books, Leonardo, unlike many of his contemporaries, recognised the limitations of pursuing truth simply through those writings or the Bible. Instead, he observed nature and asked deceptively easy scientific queries such as, “How do birds fly?” In his sketches, he then meticulously recorded their solutions.
Leonardo possessed a rare capacity to perceive and record nature. His zeal to capture those nuances prompted him to work under harsh circumstances at times. Paolo Giovi, Leonardo da Vinci’s earliest biographer, said in 1520: “He learned to dissect criminals’ cadavers under inhumane, unpleasant conditions in medical school…because he wanted to study and depict the various deflections and reflections of limbs and their dependence on nerves and joints. This is why he paid close attention to the shapes of even the tiniest organs, capillaries, and hidden skeleton sections.”
Leonardo always utilised this approach of scientific investigation as his curiosity drove him in ever wilder directions: attentive observation, repeated testing of the observation, exact drawing of the subject-object or phenomena with brief explanatory notes. The result was a collection of amazing notes on a wide range of subjects, including the nature of the sun, moon, and stars, the genesis of fossils, and, perhaps most notably, the secrets of flight.
Final Thoughts
If we look at each discipline individually, there have surely been better artists, engineers, and mathematicians. Da Vinci, on the other hand, was unrivalled as an individual in both art and science.
Before You Go…
Hey, thank you for reading this blog to the end. I hope it was helpful. Let me tell you a little bit about Nicholas Idoko Technologies. We help businesses and companies build an online presence by developing web, mobile, desktop, and blockchain applications.
We also help aspiring software developers and programmers learn the skills they need to have a successful career. Take your first step to becoming a programming boss by joining our Learn To Code academy today!
Be sure to contact us if you need more information or have any questions! We are readily available.











