Last Updated on March 22, 2023
The Age of Exploration was a time when European explorers sailed into uncharted waters. They wanted to discover new lands, cultures, and riches. They went to the Americas, Africa, Asia, and beyond. The explorers opened up new worlds, leading to global exchange and shaping the modern world we know today. Let’s explore this exciting time in history!
The Age of Exploration
The Age of Exploration, also known as the Age of Discovery, refers to a historical period in Europe from the late 15th century to the 17th century. During this time, European explorers and Conquistadors (conquerors), sponsored by their respective countries, embarked on expeditions to discover new trade routes, territories, and sources of wealth.
Technological advancements, such as improved shipbuilding and navigation tools, made these explorations possible, which allowed for longer and safer journeys across the seas.
The Age of Exploration led to significant cultural, economic, and political changes. This included the colonization of new lands, the establishment of global trade networks, and the spread of European culture and religion.
This era of exploration also contributed to the development of science, cartography, and astronomy, as well as to the formation of modern nation-states.
Factors That Led to the Age of Exploration
This era was driven by various factors that spurred European countries to venture into uncharted waters. They hoped to expand their territories, find new trade routes, and accumulate wealth and power.
Here are the key factors that led to the Age of Exploration:
The Age of Exploration Was Fueled by Economic Factors
The desire for wealth was one of the primary drivers of the Age of Exploration. European countries sought new trade routes to access valuable resources, such as spices, precious metals, and textiles.
The cost of these resources had been prohibitive due to the high tariffs and tolls charged by the Ottoman Empire and other middlemen along the traditional land routes to Asia. Finding a sea route to Asia would cut out these middlemen and bring down the cost of these resources, leading to greater profits.
Political Factors:
The Age of Exploration was also driven by the desire of European countries to expand their territories and increase their power. National competition for territory and resources was fierce, with European countries vying to control newly discovered lands. The Portuguese and Spanish, in particular, were driven by a desire to spread Christianity, and their explorations were often motivated by a desire to convert non-Christians.
Religious Factors Influenced the Age of Exploration
Religion significantly drove the Age of Exploration. The Catholic Church had long been encouraging Christians to spread their faith to non-Christians, and discovering new lands presented an opportunity to do so.
In addition, the Protestant Reformation in the early 16th century challenged the authority of the Catholic Church. This motivated Protestant countries such as England and the Netherlands to establish their own colonies in the New World.
Technological Factors
Advances in shipbuilding, navigation, and cartography played a huge role in enabling European explorers to venture into the unknown. Improvements in ship design allowed for larger and more seaworthy vessels that could travel longer distances. And on the other hand, improvements in navigation tools such as the astrolabe and compass made it easier for sailors to determine their position at sea. Innovations in cartography, such as the creation of more accurate maps, also enabled sailors to better navigate and explore new territories.
Key Explorers and their Expeditions
Numerous expeditions and voyages marked the Age of Exploration. Intrepid explorers from different European countries went on different journeys with no apparent destination from the onset.
These explorers, driven by a desire for knowledge, wealth, and adventure, braved the seas and ventured into uncharted territories, discovering new lands, cultures, and resources.
Here are some of the key explorers and their expeditions that shaped the Age of Exploration:
Christopher Columbus

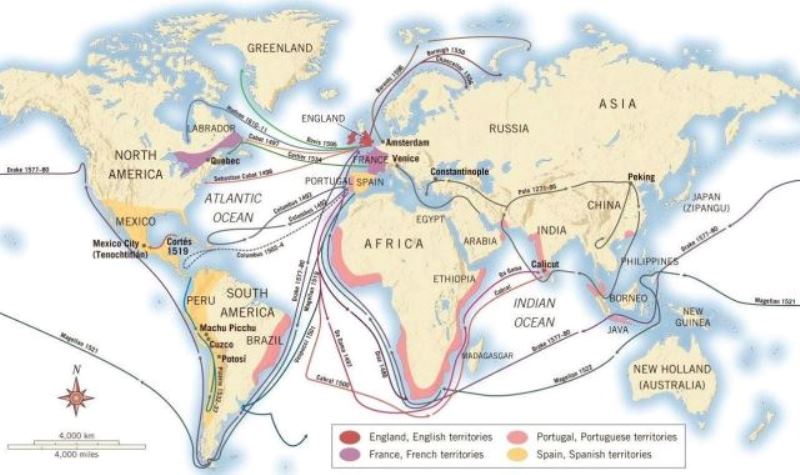
One of the most well-known explorers, Columbus, is often credited with discovering the New World. In 1492, he set sail from Spain with three ships, the Niña, the Pinta, and the Santa Maria, in search of a westward trade route to Asia.
After months at sea, he landed on an island in the Caribbean, which he named San Salvador. Over the course of four voyages, Columbus explored various Caribbean islands and Central and South America, opening up the New World to European exploration and colonization.
Vasco da Gama
A Portuguese explorer, Vasco da Gama is best known for his voyage to India in 1497-1498. He sailed around the Cape of Good Hope, along the east coast of Africa, and across the Indian Ocean, reaching Calicut, India.

This voyage opened up new trade routes between Europe and India, and Portugal gained a foothold in the lucrative spice trade.
Ferdinand Magellan
Magellan was a Portuguese explorer who led the first circumnavigation of the globe. In 1519, he set sail from Spain with five ships, hoping to find a western route to the Spice Islands.
After crossing the Atlantic and navigating the treacherous waters of the Strait of Magellan, he reached the Pacific Ocean.
He then sailed across the Pacific, landing in the Philippines, where he was killed in a skirmish with local tribes. However, one of his ships, the Victoria, continued and completed the first circumnavigation of the globe in 1522.
Sir Francis Drake
An English explorer and privateer, Drake was one of the most successful navigators of his time. In 1577, he set sail from England with five ships, hoping to find a northwest passage to Asia.
While he did not find the passage, he sailed around South America and up the west coast of North America, claiming the land for England and mapping the coastline.
He then sailed across the Pacific and around the Cape of Good Hope, returning to England in 1580 as the first Englishman to circumnavigate the globe.
Zheng He
A Chinese explorer, Zheng He, led several expeditions across the Indian Ocean in the early 15th century. His voyages, which were among the largest and most impressive of their time, took him as far as Africa and the Middle East.

It opened up new trade routes and increased Chinese influence. Zheng He’s expeditions were primarily diplomatic and aimed to establish trade relations with other countries rather than to conquer or colonize.
These are just a few examples of the many explorers and expeditions that shaped the Age of Exploration. Their voyages, discoveries, and encounters with new worlds and cultures continue to fascinate and inspire us today, highlighting the power of human curiosity, innovation, and courage.
Impacts of the Age of Exploration
The impacts of the Age of Exploration were extensive and profound, shaping the course of human history in numerous ways. Here are some of the key impacts of the Age of Exploration:
Global Trade and Commerce
The discovery of new trade routes and markets and the establishment of colonies and trading posts led to the growth of global economic networks and the development of new industries.
The trade of spices, silks, and other luxury goods from Asia, Africa, and the Americas became a significant driver of the global economy. It also enriched European merchants and stimulated economic growth in Europe.
Colonization and Imperialism
The establishment of colonies in new lands by European powers, such as Spain, Portugal, France, and England, led to the spread of European culture and values. It also ushered in an unabated period of exploitation of resources and labor in these regions.
Native people were often subjugated, enslaved, or displaced, establishing long-lasting systems of imperialism and colonialism.
Read: How the United States Erased Native Americans From Its History
Scientific and Technological Advancements
The Age of Exploration spurred scientific advancements in navigation, cartography, astronomy, and other fields. Explorers developed new instruments and techniques for navigation, such as the astrolabe and the sextant, allowing for more accurate sea travel.
Creating more detailed maps and charts also enabled explorers to chart new territories and improve navigation.
The Age of Exploration also led to technological advancements in shipbuilding and other industries, contributing to global trade and commerce growth.
Cultural Exchange
Europeans were exposed to new foods, art, literature, and languages, contributing to the development of modern global culture. At the same time, European culture and values were spread worldwide, creating new hybrid cultures and societies.

Environmental Impact
This era had a significant impact on the environment, as European explorers brought with them new plants, animals, and diseases to the regions they visited. Some of these species thrived in their new environments, while others negatively impacted native species and ecosystems.
Additionally, the exploitation of natural resources, such as timber, minerals, and precious metals, had lasting impacts on the environment and contributed to the depletion of natural resources in some regions.
Ultimately, the Age of Exploration profoundly impacted the world, shaping the course of human history in numerous ways. While its impacts were often complex and mixed, there is no doubt that the Age of Exploration was a significant period in global history that continues to shape our world today.
Before you go…
Hey, thank you for reading this blog to the end. I hope it was helpful. Let me tell you a little bit about Nicholas Idoko Technologies. We help businesses and companies build an online presence by developing web, mobile, desktop, and blockchain applications.
We also help aspiring software developers and programmers learn the skills they need to have a successful career. Take your first step to becoming a programming boss by joining our Learn To Code academy today!











