Last Updated on March 11, 2023
The Spanish Inquisition was a defining moment in European history, lasting over three centuries and impacting society, religion, and politics.
It was marked by religious persecution, torture, and intolerance, as the Catholic Church sought to enforce its doctrines and suppress dissent.
The Inquisition was characterized by its brutality and cruelty, leaving a legacy of fear and trauma. Its impact was felt far beyond the borders of Spain, sparking a wave of religious chaos across Europe and shaping the course of Western civilization.
In this article, we will explore the history of the Spanish Inquisition, from its origins to its eventual decline. We’ll also discuss its ongoing legacy in contemporary society. Through our exploration, we will gain a deeper understanding of the Inquisition’s impact on history and the lasting lessons it holds for us today.
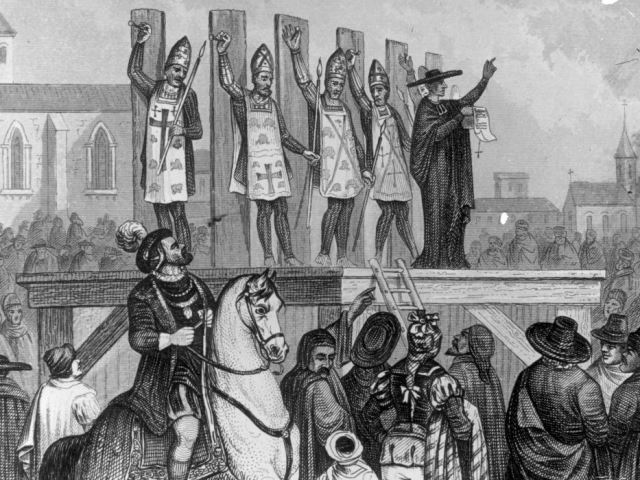

Background on the Spanish Inquisition
The Spanish Inquisition was a powerful institution of the Catholic Church that operated in Spain from 1478 to 1834. It was established by the Spanish monarchs Ferdinand II of Aragon and Isabella I of Castile to consolidate their power and maintain religious orthodoxy in their newly unified kingdom.
The Inquisition was originally intended to target Jewish converts to Christianity. This is because they were suspected of secretly practicing their former religion.
However, it quickly expanded to include Muslims, Protestants, and other religious groups deemed heretical by the Catholic Church.
The Spanish Inquisition operated through a network of courts that had the power to arrest, interrogate, and punish those suspected of heresy.
Its brutal methods included torture, imprisonment, confiscation of property, and public executions. One of those torturing methods was called Auto da Fe, which involved the burning of a heretic. The Inquisition also had a system of informants, who were encouraged to report on their neighbors and acquaintances, creating an atmosphere of fear and suspicion in Spanish society.

The Spanish Inquisition was one of the most powerful and feared institutions of its time, able to reach every corner of Spanish society. Its legacy has been controversial and divisive, with some historians arguing that it was a necessary tool for maintaining religious orthodoxy and political stability.
On the other hand, others see it as a symbol of religious intolerance and abuse of power.
Read: The American Revolution: From Colonies to Nationhood
Historical Context of the Spanish Inquisition
In the late fifteenth century, Spain was a deeply divided society with a complex mix of ethnic, religious, and political tensions.
The monarchy of Ferdinand and Isabella was still consolidating its power, having recently defeated the Moors in the Granada War and united the kingdoms of Aragon and Castile. The Catholic Church was also undergoing a period of reform, with the papacy seeking to centralize its power and assert its authority over the various national churches of Europe.
In this context, the Spanish Inquisition served several political and religious purposes. It helped to consolidate the monarchy’s power by providing a centralized institution that could enforce religious conformity and suppress dissent. It also helped to promote the Catholic Church’s reform agenda by rooting out heresy and enforcing orthodoxy.
The Inquisition was also influenced by the broader context of religious conflict in Europe. For instance, the Protestant Reformation began gaining momentum in the early sixteenth century. This happened by challenging the authority of the Catholic Church and sparking a wave of religious upheaval across the continent.
In response, the Inquisition became more aggressive in its efforts to root out heresy. This led to a wave of persecution and repression, further polarizing European society.
Impact on Religion
One of the most significant impacts of the Inquisition was the suppression of non-Catholic religions in Spain. Jews and Muslims had lived in Spain for centuries before the Spanish Inquisition. Unfortunately, they were forced to convert to Christianity or face persecution and expulsion.
The Inquisition was particularly focused on rooting out so-called “crypto-Jews” and “crypto-Muslims” – people who had converted to Christianity but were suspected of secretly practicing their former religion.
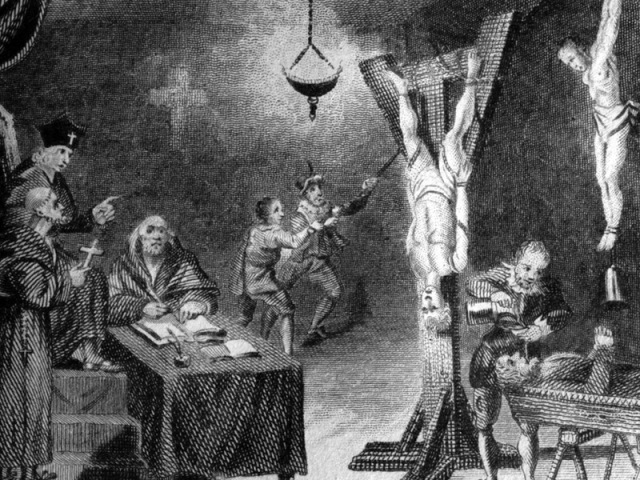

This led to widespread fear and suspicion in Spanish society, and many people were falsely accused and punished.
The Inquisition also played a role in enforcing orthodoxy within the Catholic Church. It was responsible for investigating and punishing those suspected of deviating from Church doctrine. And it had the power to censor books and other publications deemed heretical.
This chilled intellectual and artistic expression in Spain, with many writers and artists self-censoring out of fear of being accused of heresy.
Finally, the Inquisition played a significant role in the Protestant Reformation. As the Protestant movement became popular across Europe, the Inquisition also became more aggressive. The impact was widespread persecution and repression of Protestant groups. It then sparked a wave of religious conflict that lasted for centuries.
Read: The Role of Religion in African History
Impact on Society
The Spanish Inquisition had a significant impact on society in Spain. It affected the political, social, and economic spheres of life, and its impact is still felt to this day.
Politically, the Inquisition had a strong influence on the Spanish monarchy. It provided the monarchy with a tool for controlling and suppressing dissent. The Inquisition was also used to persecute non-Christians and political dissidents, who were seen as a threat to the monarchy’s authority.
Socially, the Inquisition had a significant impact on social and cultural practices. The Inquisition imposed strict codes on behavior and dressing. It also enforced stringent rules on marriage and family life. The Inquisition’s strict moral code had a particular impact on the status of women, who were often subjected to harsh punishment for violating the Inquisition’s rules.
Economically, the Inquisition affected the Spanish economy. Because many Jews were expelled from Spain, wealthy Jew merchants had a negative impact on trade and commerce in the country.
In addition to its impact on specific spheres of life, the Inquisition had a broader impact on society. It created an atmosphere of fear and suspicion, undermining social trust and solidarity. It also contributed to developing a culture of secrecy. People became reluctant to share their views or beliefs for fear of persecution.
Legacy of the Inquisition
The Spanish Inquisition had a lasting impact on Spain and its people. Its legacy can be seen in various aspects of Spanish culture and politics. It has influenced the way that others perceive Spain even till today.
One of the most significant legacies of the Inquisition is its impact on Spain’s reputation and identity. The Inquisition has been widely condemned for its brutality and its violation of human rights.
As a result, Spain has often been associated with authoritarianism and intolerance, even though the Inquisition ended more than two centuries ago.
The Inquisition’s impact on other countries is another important legacy. It inspired similar institutions in other parts of Europe.
Besides, it also served as a model for other countries that sought to establish a centralized authority over religious matters.
Additionally, the Spanish Inquisition affected literature, art, and music. Many of Spain’s most celebrated works of art and literature were created in response to the Inquisition’s repression. They reflect the tension between the Inquisition’s authority and the desire for freedom of expression.
The Inquisition’s legacy is also evident in Spanish politics. It provided the Spanish monarchy with a tool for consolidating its power and contributed to developing a centralized, authoritarian state. As such, Spain’s political culture often shows a preference for a strong, centralized authority.
Significance of the Spanish Inquisition in History
King Ferdinand II and Queen Isabella I established Spain’s powerful Inquisition in 1478 to ensure that all citizens abided by the principles of the Catholic faith. This era of history is significant because it signaled the start of a protracted period of religious intolerance and persecution. According to estimates, the Inquisition led to the death of between 30,000 to 300,000 people.
The Spanish Inquisition targeted Jews and Muslims who had converted to Christianity, known as “conversos,” and suspected them of secretly practicing their former faiths. Unfortunately, the inquisitors used torture to extract confessions and punish those who did not conform to the Catholic Church’s doctrines. The Inquisition’s brutality led to the expulsion of Jews and Muslims from Spain, significantly impacting Spanish culture and history.
Additionally, the Spanish Inquisition had a big political impact. The inquisitors were powerful tools for quelling political dissent since they had the authority to look into and bring charges against those who were thought to be involved in heresy or sedition. The Inquisition had an impact on the rest of Europe in addition to Spain, and it served as a model for inquisitions in other nations.
Overall, the Spanish Inquisition had a significant impact on Spain’s history and culture by encouraging intolerance, persecution, and repressing dissent.
Before you go…
Hey, thank you for reading this blog to the end. I hope it was helpful. Let me tell you a little bit about Nicholas Idoko Technologies. We help businesses and companies build an online presence by developing web, mobile, desktop, and blockchain applications.
We also help aspiring software developers and programmers learn the skills they need to have a successful career. Take your first step to becoming a programming boss by joining our Learn To Code academy today!











