Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Chances are you’ve heard the acronym thrown around severally. But PTSD is more than just a word. It’s the reality of millions of people who have faced traumatic events.
PTSD can impact anyone, anywhere, at any time. It could be a war veteran or just a regular person. The memories of the traumatic event can linger, causing flashbacks, anxiety, and nightmares that feel too real.
Thankfully, you don’t have to suffer alone. With the right support and treatment, individuals with PTSD can learn to manage their symptoms and live fulfilling lives.
Don’t let PTSD hold you back. Take control of your story and start healing today.
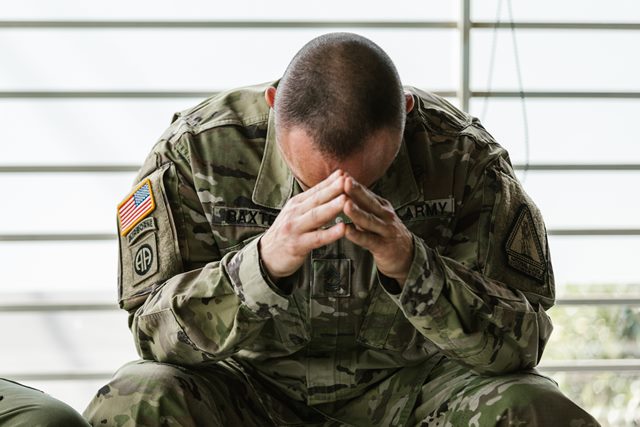

What is Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)?
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder is a mental health condition that can occur after a person experiences or witnesses a traumatic event. These events could include natural disasters, serious accidents, violent crime, military combat, or sexual assault.
PTSD can profoundly impact an individual’s daily life, affecting their relationships, work, and overall sense of well-being.
For those who suffer from this mental disorder, the traumatic event may feel like it is happening all over again, leading to intense feelings of fear, anxiety, and helplessness.
The condition can also cause flashbacks, nightmares, and avoidance behaviors, making it difficult for people to engage in everyday activities.
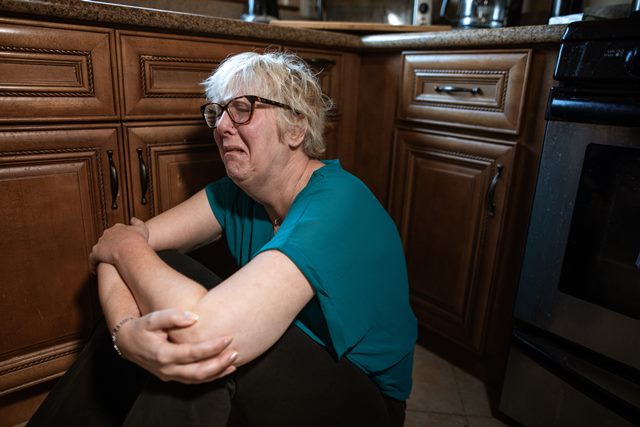

Despite being a common and treatable condition, many people who suffer from PTSD struggle to receive a proper diagnosis and the help they need. The stigma surrounding mental health conditions can prevent individuals from seeking help. And the symptoms of PTSD can be mistaken for other conditions, such as depression or anxiety.
Innovative Tech Solutions, Tailored for You
Our leading tech firm crafts custom software, web & mobile apps, designed with your unique needs in mind. Elevate your business with cutting-edge solutions no one else can offer.
Start NowAnyone can develop this condition from past trauma, regardless of background or personal characteristics. However, with the right support and treatment, they can learn to manage their symptoms and regain control of their lives.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of PTSD, it is necessary to seek help from a qualified mental health professional.
You can also dial the PTSD hotlines.
Causes of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
PTSD can affect an individual’s mental, emotional, and physical well-being. Here, we will explore the causes of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder.
Past Traumatic Events can Cause PTSD
The most significant cause of PTSD is exposure to a traumatic event. This includes natural disasters such as earthquakes, hurricanes, and wildfires; serious accidents like car crashes and falls; violence and crime such as physical or sexual assault; and military combat.
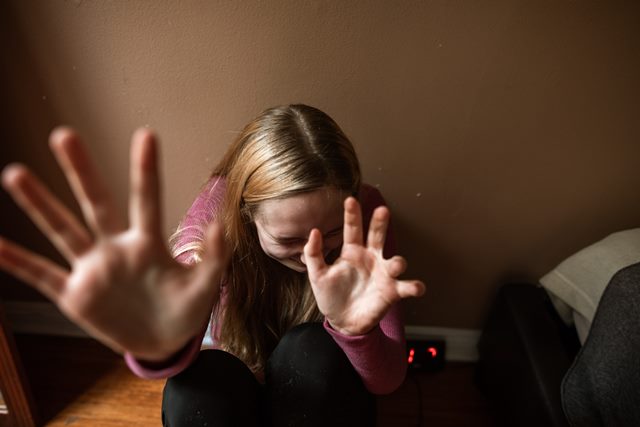

The severity of PTSD symptoms can depend on the nature and duration of the traumatic event or an individual’s proximity to the event.
Individual Factors
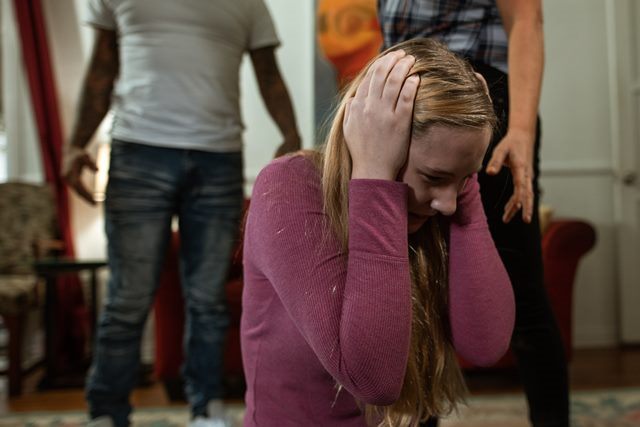
In addition to traumatic events, several individual factors can increase a person’s risk of developing PTSD. These factors include genetics, brain structure, and previous traumatic experiences.
Genetics can affect an individual’s susceptibility to Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. Research has found that certain genes are more commonly found in individuals with PTSD, suggesting that there may be a genetic component to the condition.
Brain structure is another factor that can contribute to the development of PTSD. Brain scans of individuals with PTSD have shown differences in the structure and function of certain brain regions. This includes the amygdala and the hippocampus, which play a role in regulating emotions and memory.
Previous traumatic experiences can also increase an individual’s risk of developing PTSD. Individuals who have experienced trauma in the past are more likely to experience symptoms of PTSD after exposure to a traumatic event.

Read: Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, Diagnosis
Seamless API Connectivity for Next-Level Integration
Unlock limitless possibilities by connecting your systems with a custom API built to perform flawlessly. Stand apart with our solutions that others simply can’t offer.
Get StartedSymptoms of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Below are some of the symptoms of PTSD:
Re-Experiencing the Traumatic Event
One of the most common symptoms of PTSD is re-experiencing the traumatic event. This can take many forms, including vivid flashbacks, intrusive thoughts, and nightmares.
Flashbacks are intense, vivid memories of a traumatic event that can feel like they are happening in the present moment. Intrusive thoughts are unwanted and distressing thoughts about the traumatic event. Nightmares can be particularly distressing and can cause individuals to be deprived of sleep.
Avoidance Behaviors
Another symptom of PTSD is avoidance behaviors. Individuals with PTSD may try to avoid people, places, or things that trigger memories of the traumatic event.
This can include avoiding social activities, staying away from places that trigger memories of the traumatic event or avoiding discussions about the event.
Avoidance behaviors can lead to feelings of detachment from others and social isolation. If proper attention and measures are not taken on time, this can lead to loneliness and depression.
Increased Arousal and Reactivity
Individuals with PTSD may experience increased arousal and reactivity, which can cause difficulties with sleeping, irritability, and angry outbursts.
A state of constant hypervigilance, where individuals are always on the lookout for potential danger, is also common. These symptoms can significantly impact daily life, including difficulty concentrating, difficulty sleeping, and problems with personal relationships.
Read: The Meaning and Causes of Schizophrenia
Diagnosis and Treatment of PTSD
Transform Business with Custom CRM & ERP Solutions
Elevate your operations with a CRM or ERP tailored for you. Let’s build the perfect solution that others can't replicate—crafted to match your business's needs like no other.
Get StartedA mental health professional, such as a psychologist or psychiatrist, diagnoses PTSD. The diagnostic criteria for PTSD include symptoms that persist for at least one month and cause significant impairment in daily life.

To diagnose PTSD, a mental health professional will conduct a clinical evaluation, including a thorough medical and psychiatric history. The mental health professional may also use standardized self-report measures and behavioral assessments to help diagnose PTSD.
Treatment Options for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Treatment for PTSD typically involves a combination of psychotherapy and medication. Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, is the primary treatment for PTSD and involves talking with a mental health professional to help individuals process and manage their symptoms.
Following are highlights of some of the treatment methods for PTSD:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a type of psychotherapy commonly used to treat PTSD. CBT helps individuals change negative thought patterns and behaviors contributing to their symptoms.

Furthermore, Exposure Therapy is another type of CBT that involves repeated exposure to trauma-related stimuli in a safe and controlled environment. This therapy helps individuals gradually overcome their fear and anxiety related to the traumatic event.
Medication
Medication can also be an effective treatment for PTSD. Antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can help reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression and improve sleep.

Beta-blockers can also be used to treat physical symptoms of PTSD, such as increased heart rate and sweating.
Tailored Tech Solutions to Drive Your Business Forward
Maximize your business potential with custom tech strategies. We deliver bespoke solutions that others can’t match, designed to solve your specific challenges with precision and impact.
Contact UsSupport Groups
Support groups provide a safe and supportive environment for individuals with PTSD to connect with others who understand what they are going through.
Participants can share their experiences, offer support to one another, and learn coping strategies to help manage their symptoms. Support groups can also offer a sense of community and belonging, which can be particularly beneficial for individuals who feel isolated or misunderstood.

In addition to connecting with others, support groups can provide education about PTSD and its treatment.
Participants can learn about the latest research and treatments, as well as effective coping strategies and techniques for managing symptoms. This can help individuals better understand their condition and how to manage it in their daily lives.
For those who may feel uncomfortable talking about their experiences in a group setting, virtual support groups and online communities can provide a more convenient and accessible option.
These online resources can offer the same benefits as in-person support groups, such as connecting with others and receiving education and support. But with the added convenience of participating from the comfort of their own home.
However, support groups should not be considered a substitute for professional mental health treatment. Instead, support groups can complement therapy and other forms of treatment, helping individuals manage their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life.
Other treatments for PTSD can include Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), which involves focusing on eye movements while recalling the traumatic event, and Group Therapy, which provides individuals with the opportunity to connect with others who have experienced similar trauma.
Read: What Does Bipolar Disorder Mean?
The Reality of People Living With PTSD
One of the most difficult aspects of living with PTSD is the presence of symptoms such as flashbacks, avoidance behavior, irritability, and sleep disturbances. These symptoms can be distressing and interfere with daily activities, relationships, and work.

However, with the help of a mental health professional, individuals can develop effective strategies to manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
A critical aspect of managing PTSD is seeking support from others. This can involve connecting with others who have experienced similar traumatic events. It also involves participating in support groups or reaching out to loved ones for emotional support.
Also, talking about your experiences with others can help you process your trauma, feel less alone, and receive the encouragement and support you need to manage your symptoms.
In addition to seeking support from others, individuals can also benefit from engaging in self-care activities. This can involve practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga or engaging in physical activities to improve overall physical and emotional health.
Making time for hobbies, spending time with loved ones, and taking care of your physical health can also help improve your overall well-being.
It is also advisable to seek professional help, such as therapy or medication. A mental health professional can provide personalized treatment recommendations and support as you navigate your recovery.
Before you go…
Hey, thank you for reading this blog to the end. I hope it was helpful. Let me tell you a little bit about Nicholas Idoko Technologies. We help businesses and companies build an online presence by developing web, mobile, desktop, and blockchain applications.
We also help aspiring software developers and programmers learn the skills they need to have a successful career. Take your first step to becoming a programming boss by joining our Learn To Code academy today!